Copyright Resources
Resources on copyright in Singapore are provided here, including guides and information on copyright protection, infringement, and management for creators and businesses.
On this page
Copyright Infopack
Download and read this Copyright 101 Infopack [PDF, 606 KB], which covers the following information:
What is copyright?
Who are the key players in Singapore's copyright system?
What content does copyright protect?
How is copyright protection obtained?
Who owns copyright?
When does copyright expire?
When is copyright infringed and what are the exceptions?
What remedies are available for infringement?
What do the copyright tribunals do?
What are moral rights?
If you would like to learn more about the Copyright Act 2021, such as the default ownership of commissioned works, the new moral right to be identified as a creator, and a new educational exception, please see our Copyright Act 2021 factsheet [PDF, 572 KB]
Factsheets on Copyright Act 2021
Learn more about the Copyright Act 2021
Find out how the new Copyright Act may affect you.
Did you know that you have to clearly attribute creators when using their work in public?
Are you a Content Creator or Performer?
Want some quick practical tips on protecting your copyright?
Are you a Business Owner?
What must you take note of when negotiating a commissioning contract with a content creator?
Are you engaging a Portrait Photographer for an event?
Find out more about how your personal data will be protected and tips on negotiating your contract.
Guide to the CMO Class Licensing Scheme
Collective Management Organisations (CMOs) are organisations appointed by rights owners to manage the use of their content, such as music, films and books. Find out more about the regulatory regime for CMOs, including the key aspects of the class licensing scheme administered by IPOS.
Click here to download and read this CMO Guide.
A Practical Guide to the Copyright Tribunals
The Copyright Tribunals in Singapore provide a quick, informal, and cost-effective solution to resolving licensing disputes without going through litigation. Find out more about how to use the Copyright Tribunals, including how to start a case and what happens after a case is filed here.
Other resources
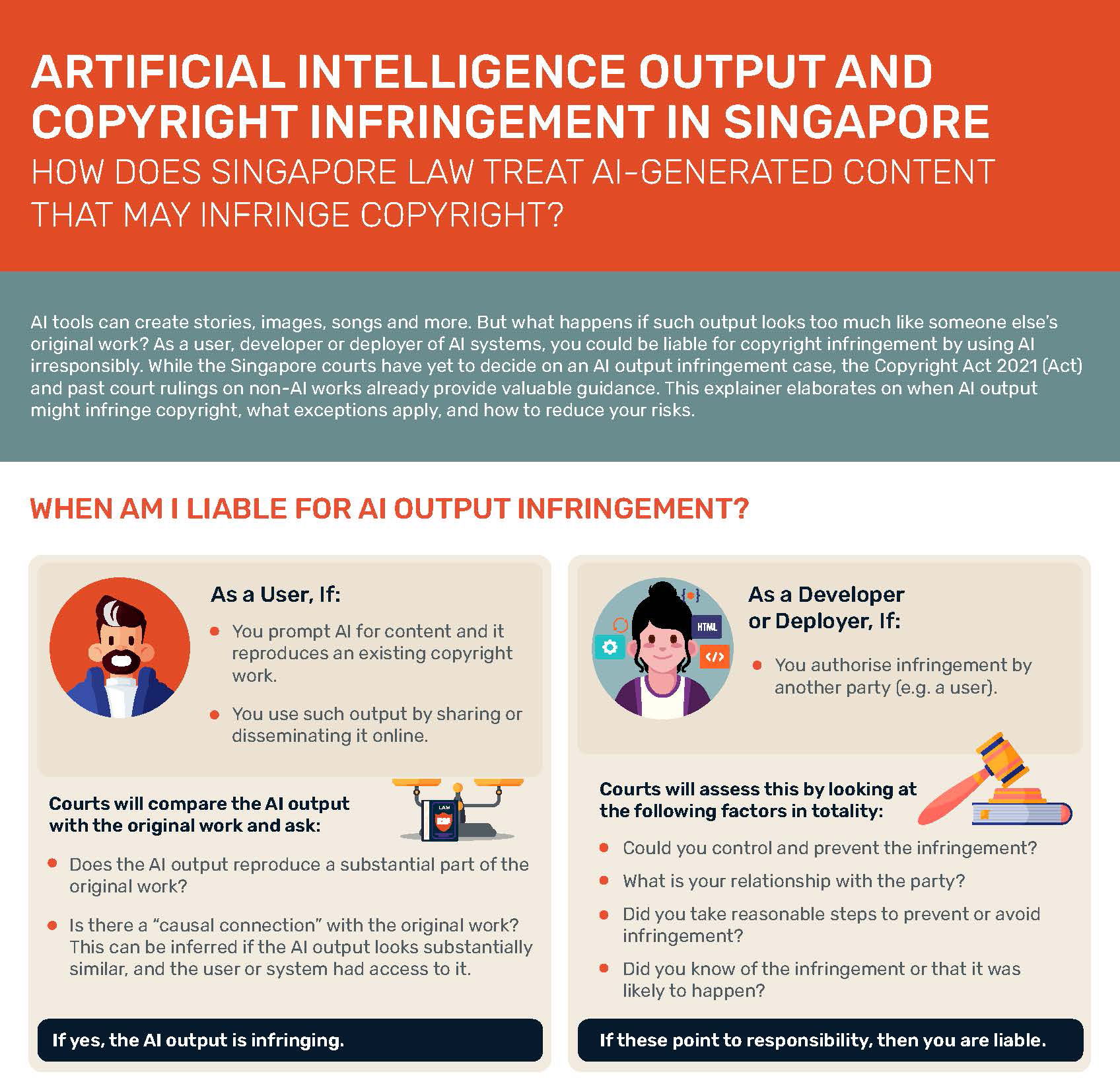
Artificial Intelligence
With the technological revolution in AI, questions are arising about the intersection of AI and copyright.
IPOS is gathering input on real and practical issues faced by our copyright owners and local community of AI developers and users in order to remain current on the technological developments and business concerns relating to AI.
Find out more about AI and Copyright through our series of bite-sized explainers here:

Non-fungible tokens
Non-fungible tokens (or more commonly known as NFTs) are typically unique tokens on a blockchain which link or point to any type of digital assets, such as images, films and music. Find out more about NFTs, the relationship between NFTs and Intellectual Property (IP), and what you should note when creating or owning an NFT.
Download and read this information note on IP and NFTs [PDF, 599 KB].
Frequently Asked Questions on creation and online distribution of digital content
Find out more about specific copyright issues creators face in creating digital content and distributing it online here.
